LinkedHashMap概述
JDK对LinkedHashMap的介绍:
Hash table and linked list implementation of the Map interface, with predictable iteration order. This implementation differs from HashMap in that it maintains a doubly-linked list running through all of its entries. This linked list defines the iteration ordering, which is normally the order in which keys were inserted into the map (insertion-order). Note that insertion order is not affected if a key is re-inserted into the map. (A key k is reinserted into a map m if m.put(k, v) is invoked when m.containsKey(k) would return true immediately prior to the invocation.)
大意是:LinkedHashMap是通过哈希表和链表来实现Map接口,它通过维护一个链表来保证对哈希表迭代时的有序性,而这个有序是指键值对插入的顺序。另外,当向哈希表中重复插入某个键的时候,不会影响到原来的有序性。
JDK对LinkedHashMap的介绍:
Hash table and linked list implementation of the Map interface, with predictable iteration order. This implementation differs from HashMap in that it maintains a doubly-linked list running through all of its entries. This linked list defines the iteration ordering, which is normally the order in which keys were inserted into the map (insertion-order). Note that insertion order is not affected if a key is re-inserted into the map. (A key k is reinserted into a map m if m.put(k, v) is invoked when m.containsKey(k) would return true immediately prior to the invocation.)
大意是:LinkedHashMap是通过哈希表和链表来实现Map接口,它通过维护一个链表来保证对哈希表迭代时的有序性,而这个有序是指键值对插入的顺序。另外,当向哈希表中重复插入某个键的时候,不会影响到原来的有序性。
继承结构

可以看到LinkedHashMap直接继承了HashMap,复用了HashMap的很多方法,比如put、resize等方法,LinkedHashMap是在HashMap的基础上实现了自己的功能:有序插入。

可以看到LinkedHashMap直接继承了HashMap,复用了HashMap的很多方法,比如put、resize等方法,LinkedHashMap是在HashMap的基础上实现了自己的功能:有序插入。
数据结构
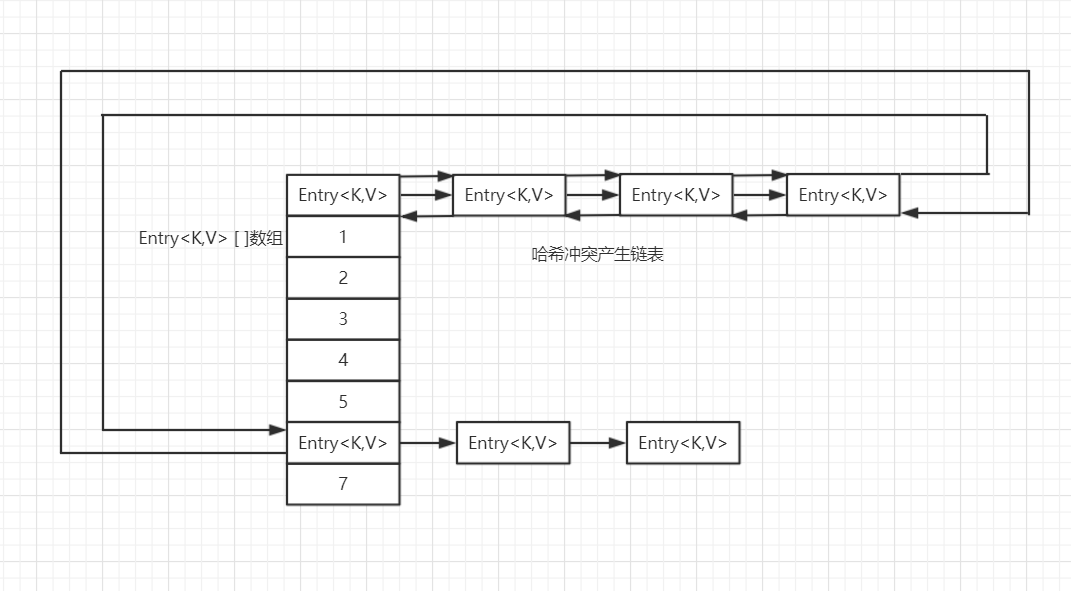
可以看到,LinkedHashMap数据结构相比较于HashMap来说,添加了双向指针,其中before指向节点的前继节点,after指向节点的后继节点,从而将所有的节点串联在一起形成一个双向链表。

可以看到,LinkedHashMap数据结构相比较于HashMap来说,添加了双向指针,其中before指向节点的前继节点,after指向节点的后继节点,从而将所有的节点串联在一起形成一个双向链表。
内部字段及构造方法
内部字段
//双链表头节点 transient Entry<K,V> head; //双链表尾节点 transient Entry<K,V> tail; //accessOrder为true则表示按照基于访问的顺序来排列,意思就是最近使用的entry, //放在链表的最末尾,为false表示按照基于插入的顺序来排列,后插入的放在链表末尾,不指定默认为false final boolean accessOrder; static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> { //双链表前继、后继节点 Entry<K,V> before, after; Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, value, next); } }
//双链表头节点 transient Entry<K,V> head; //双链表尾节点 transient Entry<K,V> tail; //accessOrder为true则表示按照基于访问的顺序来排列,意思就是最近使用的entry, //放在链表的最末尾,为false表示按照基于插入的顺序来排列,后插入的放在链表末尾,不指定默认为false final boolean accessOrder; static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> { //双链表前继、后继节点 Entry<K,V> before, after; Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, value, next); } }